Insider threats, driven by personal motivations and enabled by the rapid evolution of technology and changing hybrid work environments, present a critical challenge to organizational security. Addressing these threats requires a sophisticated, multi faceted approach that combines advanced detection technologies, continuous monitoring, and a strong emphasis on employee training and awareness.
A new report by Cybersecurity Insiders and Securonix, based on a survey of 467 cybersecurity professionals, uncovers the nature of insider threat challenges faced by organizations, focusing on understanding the factors driving these threats, their detection and mitigation complexities, and the effectiveness of insider threat programs.
The report provides intriguing insights into how organizations are adapting their strategies and solutions to effectively counter evolving internal security risks:
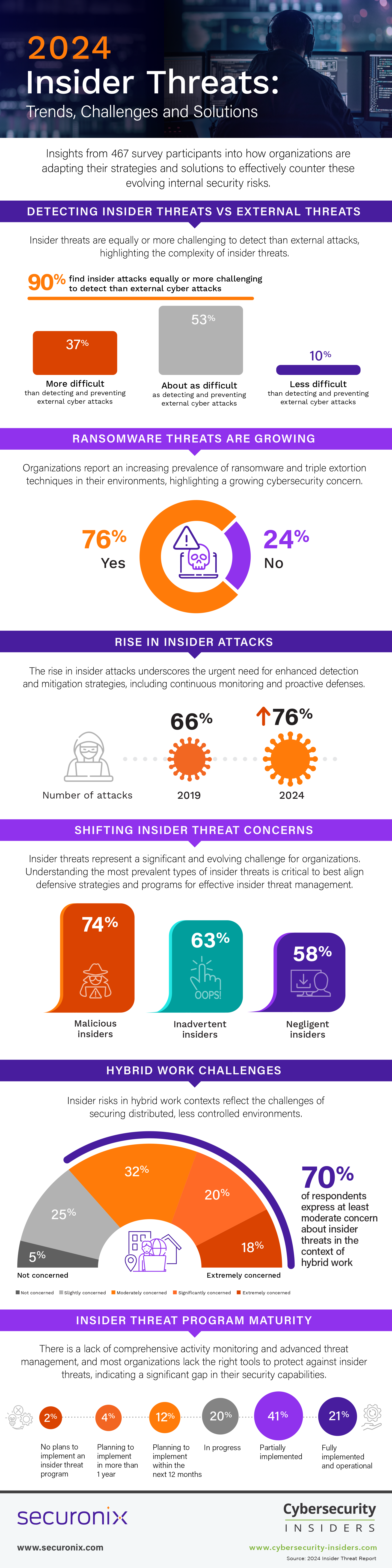
- Rise in Insider Attacks: From 2019 to 2024, the number of organizations reporting insider attacks increased from 66% of organizations to 76%, indicating a substantial increase in detected insider threats. Notably, there’s a rise in incidents with multiple attacks per year, underscoring the urgent need for enhanced detection and mitigation strategies, including continuous monitoring and proactive defenses.
- High-Risk Insiders and Motivations: There has been a marked increase in concern for malicious insiders, rising from 60% in 2019 to 74% in 2024, indicating a heightened awareness or experience of intentional insider attacks. Financial gain leads the list of motivations organizations are most concerned about.
- Detecting Insider vs. External Attacks: 90% of respondents report insider attacks as equally or more challenging to detect than external attacks, highlighting the complexity of insider threats. Only 16% of organizations consider themselves extremely effective in handling insider threats, an improvement from 11% in 2019, yet there is still significant room for enhancing threat management strategies.
- Ransomware Threat: 76% of organizations report an increasing prevalence of ransomware and triple extortion techniques in their environments, highlighting a growing cybersecurity concern. Information disclosure (56%) and unauthorized data operations (48%) are also leading concerns, emphasizing the importance of data-centric security measures and robust identity and access management controls.
- Hybrid Work and Evolving Tech: 70% of respondents express concern about insider risks in hybrid work contexts, reflecting the challenges of securing distributed, less controlled environments. A majority of 75% are concerned about the impact of emerging technologies like AI, the Metaverse, and Quantum Computing on insider threats, indicating worries about their misuse and the potential to amplify threat capabilities.
- Insider Threat Program Maturity: While 66% of organizations feel vulnerable to insider attacks, 41% of organizations have only partially implemented insider threat programs, pointing to a lack of comprehensive activity monitoring and advanced threat management. Only 29% of respondents feel fully equipped with the right tools to protect against insider threats, indicating a significant gap in many organizations’ security capabilities.
Insider vs External Attacks
The perception of the difficulty in detecting and preventing insider attacks, as compared to external cyber attacks, has shifted noticeably in the last 5 years. In 2024, an overwhelming majority of 90% of respondents report that insider attacks are as difficult (53%) or more difficult (37%) to detect and prevent compared to external attacks, up from a combined 50% who held this view in 2019. This significant increase suggests a growing awareness of the subtlety and complexity of insider threats compared to external ones.
Malicious insider threats, characterized by otherwise legitimate users exploiting their access and deep organizational knowledge, present unique detection challenges. These insiders navigate around security policies and controls to mask their malicious activities within normal operations. Their familiarity with security practices, coupled with the trust they’re afforded and the growing shift to remote work scenarios, further complicates the differentiation between benign and malicious actions. In contrast to external threats, which often exhibit more apparent indicators of compromise, insider activities necessitate a more sophisticated approach to detection, underscoring the need for advanced, nuanced methods to identify these subtle threats.
To address the inherent difficulty in detecting and preventing insider threats, organizations should consider implementing advanced security solutions that offer deep visibility into user behaviors and activities. This includes employing behavioral analytics and sophisticated monitoring techniques to detect even subtle signs of insider threats. Furthermore, organizations should foster a culture of security awareness and adopt a layered security approach that integrates both technical and administrative controls to manage both insider and external threats effectively.
Shifting Insider Threat Concerns
Insider threats represent a significant and evolving challenge for organizations. It is critically important to understand the most prevalent types of insider threats to best align defensive strategies and programs for effective insider threat management.
The survey data indicates a shift in the perception of insider threats over the last 5 years. There has been a marked increase in concern for malicious insiders, rising from 60% in 2019 to 74% in 2024, indicating a heightened awareness or experience of intentional insider attacks. However, concerns about inadvertent insider incidents have slightly decreased from 71% in 2019 to 63% in 2024, perhaps indicating improved training, awareness, policy, and technological safeguards within some organizations or across some sectors.
Organizations should continue to enhance their strategies against malicious insiders by investing in advanced behavioral analytics and insider threat detection systems. It’s also crucial to emphasize employee training and maintain a culture of security awareness to prevent inadvertent and negligent incidents.
Changing Insider Motives
Understanding the motives driving malicious insiders, the primary insider threat concern identified in our survey, is key to crafting effective countermeasures and risk management strategies. The evolution of these motivations over the past 5 years, particularly the dramatic rise in concerns regarding personal benefit, underscores changing personal dynamics and external influences on risk profiles.
The most notable change in the past 5 years is the dramatic increase in concerns regarding personal benefit as an insider motive, which has risen from rank #6 in 2019 (15%) to #2 in 2024 (47%). Traditional fears such as financial motivations (50%) and revenge (45%) remain high, while sabotage decreased slightly (from 43% to 40% respectively). Notably, a significant increase in insider threats for reputational damage (from 8% to 37%) reflects the growing importance of public perception.
Organizations should consider implementing insider threat programs that include psychological elements and incentives alignment to counteract the risk of employees being swayed by personal gain or external influences. It’s also crucial to foster a culture where ethical conduct and reporting of suspicious activities are encouraged and rewarded.
Insider Attack Vectors
The methods by which insider attacks are carried out have significant implications for organizational security. A nuanced understanding of these methods assists in preemptively addressing potential insider attacks and reducing the attack surface.
The leading concern is information disclosure at 56%, underscoring the primacy of protecting sensitive data against mishandling. Unauthorized data operations comes in second at 48% (including data tampering and destruction), reflecting unease about the multitude of ways data can be misused. Credential and account abuse follows closely at 47% (such as credential sharing or unauthorized access), spotlighting the vulnerability that comes with improper credential management and the potential for significant damage via privilege escalation.
Security evasion and bypass (45%), along with software and code manipulation (44%), are also major concerns, indicating apprehension about the ingenuity of insider threats in circumventing policy and security controls. To address these attack vectors, organizations should double down on data-centric security measures and robust identity and access management (IAM) controls. Regular audits, coupled with advanced analytics to detect anomalies in user behavior, can prove pivotal in early identification and mitigation of these threats.
Critical Data at Risk
The types of data most at risk to insider attacks reflect both the value and accessibility of that information within an organization.
Financial data is perceived as the most vulnerable, with 44% of respondents highlighting it, likely due to its direct monetization potential. Customer data, at 41%, follows closely, pointing to concerns over the loss of personally identifiable information (PII). Employee data is also a significant concern at 37%, signaling an awareness of the risks posed by the mishandling of sensitive personnel information. It is notable that a considerable 31% believe all company-sensitive data is susceptible, reflecting a broader concern for organizational data security.
Proactive measures such as data access controls, encryption, and employee training can mitigate the risk of insider attacks and threats to data confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Emphasizing the protection of the most vulnerable financial, customer, and employee data as part of a comprehensive data security strategy is imperative.
Heightened Vulnerability Awareness
Assessing an organization’s susceptibility to insider threats is a critical barometer of its security posture. The evolving perceptions of vulnerability reflect changing threat landscapes and internal security measures.
In 2019, the combined percentage of organizations feeling at least moderately vulnerable was 69%, compared to 66% in 2024. However, the leap in those perceiving extreme vulnerability from 5% in 2019 to 16% in 2024 signals heightened awareness or potentially an increase in threat activity.
Hybrid Workforce Insider Threats
The shift towards hybrid working models has led to a reevaluation of insider risk perceptions due to the expanded threat surface and altered work dynamics. The level of concern reflects the complexity of managing security in less controlled environments.
Collectively, 70% of respondents express at least moderate concern about insider threats in the context of hybrid work, with 18% being extremely concerned and 20% significantly concerned. This indicates a strong awareness of the potential for increased insider threats as traditional office boundaries are blurred. The moderate concern at 32% suggests that while some are aware of the risks, they may feel somewhat prepared to manage them.
Ransomware and Triple Extortion Techniques
The rising trend in triple extortion techniques can be partially attributed to various insider threat-related issues, including negligence, lack of training, misuse of access and international collaboration, and challenges of secure remote working environments.
Tech Revolution Raises Alarm
Emerging technologies like AI, the Metaverse, and Quantum Computing pose new challenges in cybersecurity, potentially reshaping the threat landscape with their capabilities and complexities.
A majority of 75% of survey respondents harbor at least moderate concern about the impact of emerging technologies on insider threats, with 19% being extremely concerned. It’s clear that the misuse of AI by insiders is a significant worry, given AI’s potential to amplify threat capabilities. The Metaverse introduces new dimensions of data integration and storage, raising concerns about the exploitation of its nascent security protocols for novel attacks by insiders. Meanwhile, Quantum Computing, although a future concern, looms over current encryption methods, with the potential for insiders to break encryption and gain access to sensitive data by harnessing quantum computing power.
To navigate these concerns, companies should invest in research and training focused on the security challenges posed by emerging technologies and should integrate adaptive security measures that can evolve with these advancements.
Rise in Insider Attacks
The frequency of insider attacks is a crucial indicator of the internal threat environment and an organization’s defensive posture against such incidents. From 2019 to 2024, there’s been a noticeable decrease in organizations reporting no insider attacks, from 34% down to 24%. This suggests a significant overall increase in detected insider threat activities for 76% of organizations (up from 66% in 2019).
While the most common attack frequency, 1-5 attacks, decreased from 44% to 31%, there is a significant rise in the 6-10 attacks category, jumping from 14% to 26%. An even more pronounced jump occurred in the 11-20 attacks bracket, from 5% to 17%, indicating a rise in organizations experiencing multiple incidents within a year.
Organizations should intensify their focus on insider threat detection and mitigation strategies, investing in technologies and processes that can scale with this apparent increase in incident frequency. The trend towards more frequent attacks underlines the need for continuous monitoring and proactive defense mechanisms.
40% of respondents observed an increase in the frequency of insider attacks over the last year, pointing to a dynamic threat landscape where internal risks are growing. In contrast, 35% report no change, which could suggest effective current security measures or a stable threat environment. Meanwhile, 25% perceive a decrease in frequency, potentially indicating successful interventions or improvements in their cybersecurity posture.
Catalysts of Insider Attacks
Understanding the main drivers behind the observed escalation in insider attacks helps organizations to tailor their defensive strategies more effectively and address the root causes.
The survey highlights a lack of training and awareness as the top enabler for insider attacks, with 37% of respondents citing it. This underlines the necessity of comprehensive security awareness programs. The complexity of global operations and new technologies (such as IoT and AI) is also a significant factor, mentioned by 34%, suggesting that the rapid tech adoption outpaces security measures. Inadequate security measures and complex IT environments are acknowledged by 29% and 27% of respondents, respectively, emphasizing the need for robust data protection and streamlined IT practices. Disgruntled insiders are seen as a key risk by 25% of participants, indicating the importance of employee satisfaction and engagement.
Cultivating a Security-Conscious Workforce
Effective cybersecurity hinges significantly on employee training, especially for reducing insider threats. Although 53% of organizations provide insider risk training, the remaining 47% overlook a key aspect of their security strategy. Training is essential for equipping employees with the understanding and skills needed to identify and mitigate potential security risks, even those arising from routine activities.
Such training cultivates a strong security culture, ensuring staff are not only prepared to prevent incidents but also respond effectively when they occur. This is crucial for compliance with data protection and privacy regulations. Empowering employees through training also leads to a notable decrease in accidental threats, often caused by unawareness rather than intent.
Further, trained employees are better equipped to handle remote work challenges, comply with regulations, and use technology securely. Implementing insider threat awareness programs should be a top priority for organizations, enhancing their overall security framework and ingraining a sustainable, security-centric mindset across the workforce.
Insider Threat Program Maturity
The maturity of an organization’s insider threat program is a critical measure of its capability to identify and mitigate internal security risks.
The survey reveals that a substantial 41% of organizations are at a stage where their insider threat program is only partially implemented, indicating they have foundational tools and policies but lack comprehensive activity monitoring. This is followed by 20% who are currently developing or pilot testing their programs, showing a proactive approach towards establishing more robust insider threat management. Interestingly, only 21% report having a fully operational program in place, demonstrating a strong commitment to advanced monitoring and periodic assessments.
Organizations should strive to advance their insider threat programs through these stages, aiming for full implementation to ensure comprehensive internal security.
Insider Threat Management Effectiveness
The effectiveness of an organization in managing insider threats is a crucial indicator of its security posture and resilience. In 2024, an alarming majority of 54% report their insider threat programs are less than effective, virtually unchanged from the 56% who held this view in 2019.
However, 16% of organizations consider themselves extremely effective in handling insider threats today, up from 11% in 2019. This improvement suggests that some organizations have enhanced their insider threat programs, possibly incorporating more advanced technologies and refined processes. About a third of organizations, 30% today compared to 33% in 2019, rate themselves as very effective.
The category of “somewhat effective” remains the largest, with a minor decrease from 40% to 38% in 2024. This consistency suggests that while many organizations are making efforts, there’s still room for improvement in their threat management strategies. Concurrently, the percentages for not very effective (14%) and not at all effective (2%) also remained unchanged over the five years. This stagnation points to a large cohort of organizations that continue to struggle with insider threat management, possibly due to resource constraints, lack of expertise, or insufficient prioritization of insider threats.
Insider Threat Program Drivers
The reasons behind the implementation or enhancement of an organization’s Insider Threat Program reflect the complex interplay of internal motivations and external pressures in shaping cybersecurity strategies.
Management directives are the leading motivator, cited by 40% of respondents. This top-down approach underscores the critical role of executive leadership in prioritizing and driving cybersecurity initiatives. Close behind, 38% indicate that regulatory and governance requirements are key factors, reflecting the influence of legal and compliance pressures in shaping security programs.
Proactive team initiatives, highlighted by 31%, show the importance of security and IT teams in recognizing and acting upon internal risk factors. This is a positive indication of operational teams taking ownership of cybersecurity challenges. Insurance requirements are also a significant driver, mentioned by 29%, pointing to the growing impact of cyber liability insurance in dictating security standards. Incident-based motivations, at 28%, suggest that experiencing or suspecting internal security incidents is a strong catalyst for action.
Interestingly, 22% of participants report having no formalized insider threat program, which could be due to a variety of reasons ranging from resource limitations to a lack of perceived need. Organizations should consider these diverse factors when developing or enhancing their Insider Threat Programs, balancing internal initiatives with external requirements and influences to create a robust and responsive security posture.
Insider Threat Tool Effectiveness
The right tools for protecting sensitive information and systems from insider threats are crucial. In the survey, only 29% of organizations feel fully equipped with the necessary tools to handle insider threats, highlighting significant room for improvement in many enterprises’ security toolkits. The largest segment, 52%, acknowledges having some tools but also identifies gaps, indicating a widespread need for more comprehensive solutions that can provide deeper insights into user behaviors and potential threats. Meanwhile, 19% of organizations lack critical tools for effective monitoring and protection, indicating a significant vulnerability.
To bridge these gaps, organizations should consider adopting advanced security solutions that offer deep visibility into user activities and behaviors. These technologies can enhance the detection of anomalous behaviors and facilitate a proactive response to potential insider threats.
User Behavior Monitoring
User behavior monitoring for security purposes is a critical aspect of cybersecurity, reflecting an organization’s capability to preemptively identify and mitigate insider threats.
The survey reveals varied approaches among organizations: 30% of organizations have implemented continuous monitoring using automated tools, offering the most effective real-time surveillance and anomaly detection. This proactive strategy is paramount for early threat detection and response. In contrast, 26% rely on incident based monitoring, indicating a reactive approach that focuses on analyzing user behavior post-incident for forensic purposes. While useful for understanding insider activity, it lacks preventive capabilities.
20% of respondents maintain only basic access logs, providing minimal insights and lacking depth for comprehensive threat analysis. 15% conduct conditional monitoring under specific circumstances or for particular users, offering targeted but limited coverage. Notably, 7% are still in the planning phase of implementing user behavior monitoring, acknowledging its importance but yet to operationalize it.
These findings highlight the importance of continuous and proactive user behavior monitoring in the current cybersecurity landscape. Organizations, especially those without robust monitoring systems, should prioritize developing and implementing comprehensive user behavior monitoring solutions to enhance their security posture against insider threats.
Balancing Privacy and Security in User Monitoring
User privacy in monitoring insider threats is a complex and nuanced issue that requires careful consideration of both individual rights and the need for organizational protection.
A majority of 66% view user privacy as a priority. For a significant 41% of respondents, user privacy is a major concern, indicating that many organizations prioritize safeguarding individual rights while monitoring for insider threats. This approach likely involves strict adherence to privacy laws and ethical guidelines, ensuring that security measures do not infringe on personal privacy rights.
This is followed by 25% who acknowledge user privacy as a concern but not the sole focus of their monitoring programs. This response suggests a more balanced approach where user privacy is important, but it is weighed alongside other factors like organizational security and threat detection efficiency. 20% indicate that their approach to user privacy depends on specific circumstances or threat levels. This might involve a dynamic strategy where privacy considerations vary based on the context, such as the severity of the perceived threat or specific regulatory requirements. 8% consider user privacy a minor concern, secondary to organizational security. This stance suggests that while privacy is not disregarded, it takes a backseat in the face of insider threat risks.
Only 7% do not consider user privacy at all when monitoring for insider threats, reflecting a stance that prioritizes organizational security above all else. This approach might be more prevalent in sectors where security is of paramount importance, but it risks non-compliance with privacy regulations and ethical standards.
Organizations should strive for a balanced approach that respects user privacy while effectively managing insider threats. Adopting transparent policies, ensuring compliance with data protection regulations, and employing minimally invasive monitoring techniques can help maintain this balance. Solutions that provide advanced threat detection while safeguarding user privacy, such as anonymizing data or using aggregated analytics, can be beneficial. This approach not only aligns with legal and ethical standards but also fosters a culture of trust and respect within the organization.
Overcoming Obstacles to Insider Threat Management
Implementing effective insider threat management tools and strategies is critical for organizations to protect against potential attacks and security incidents from within.
Technical complexities are the most cited barrier, with 32% of respondents grappling with data classification and deployment issues, which can deter the effective monitoring of user activities. Compliance and privacy issues are a close second at 31%, highlighting the difficulty in aligning security practices with legal frameworks while maintaining employee privacy. Cost factors are a concern for 29% of organizations, as the investment in advanced tools must be justified against tangible returns. Resource limitations, including staffing and expertise, challenge 27% of organizations, suggesting a need for user-friendly and manageable security solutions. Uncertainty about the effectiveness of various tools affects 22% of respondents, indicating a gap in clear, authoritative guidance on tool efficacy.
Organizations should seek scalable and interoperable solutions that offer a balance between advanced security features and user-friendliness. Prioritizing staff training, clear policies, and leadership support can also drive the successful adoption of insider threat programs.
Navigating Insider Threat Challenges
The challenge of protecting against insider threats is compounded by several factors, as indicated by the survey. Highest ranked is the rapid rate of technological change, noted by 36% of respondents, suggesting that organizations struggle to keep pace with the security implications of new technologies. This is compounded by data leakage risks, as 32% of organizations grapple with the use of leak-prone cloud applications and personal devices. The complexity of securing remote work environments is a close third at 31%, reflecting the difficulties in extending traditional security measures to home networks and personal devices used for work.
Employee awareness and training, with 29% indicating this as a challenge, highlights the need for continuous education on evolving security threats. Additionally, 27% point to the issue of legitimate access, where individuals with authorized access make it challenging to identify and prove malicious intent. A quarter of respondents pinpoint detection challenges, including the difficulty in identifying rogue devices and a lack of cloud security tools, as a significant hurdle.
To mitigate these challenges, organizations should adopt a multifaceted approach, including continuous risk assessments, staff training programs, investment in advanced detection and response solutions, and the development of a cohesive governance structure that integrates various security tools and practices. These efforts should be aligned with legal and regulatory requirements and adapted to the unique risks posed by rapid technological advancement and the complexities of modern work environments.
Best Practices for Insider Threat Management
In an environment where insider threats are increasingly sophisticated and damaging, adopting these best practices is essential for organizations to effectively safeguard their assets and maintain robust cybersecurity.
Research Methodology & Demographics
This 2024 Insider Threat Report is based on a comprehensive online survey of 467 cybersecurity professionals, conducted in December 2023, to gain deep insight into the latest trends, key challenges, and solutions for insider threat management.
The survey utilized a methodology ensuring a diverse representation of respondents, from technical executives to IT security practitioners, across various industries and organization sizes. This approach ensures a holistic and balanced view of the insider threat landscape, capturing insights from different organizational perspectives and experiences.
In “Select all that apply” survey questions, the total percentage can exceed 100% because respondents could pick more than one answer.
Cybersecurity Insiders brings together 600,000+ IT security professionals and world-class technology vendors to facilitate smart problem-solving and collaboration in tackling today’s most critical cybersecurity challenges.
Our approach focuses on creating and curating unique content that educates and informs cybersecurity professionals about the latest cybersecurity trends, solutions, and best practices. From comprehensive research studies and unbiased product reviews to practical e-guides, engaging webinars, and educational articles – we are committed to providing resources that provide evidence-based answers to today’s complex cybersecurity challenges.
Contact us today to learn how Cybersecurity Insiders can help you stand out in a crowded market and boost demand, brand visibility, and thought leadership presence.
Email us at info@cybersecurity-insiders.com or visit https://cybersecurity-insiders.com